What Are Salivary Glands?
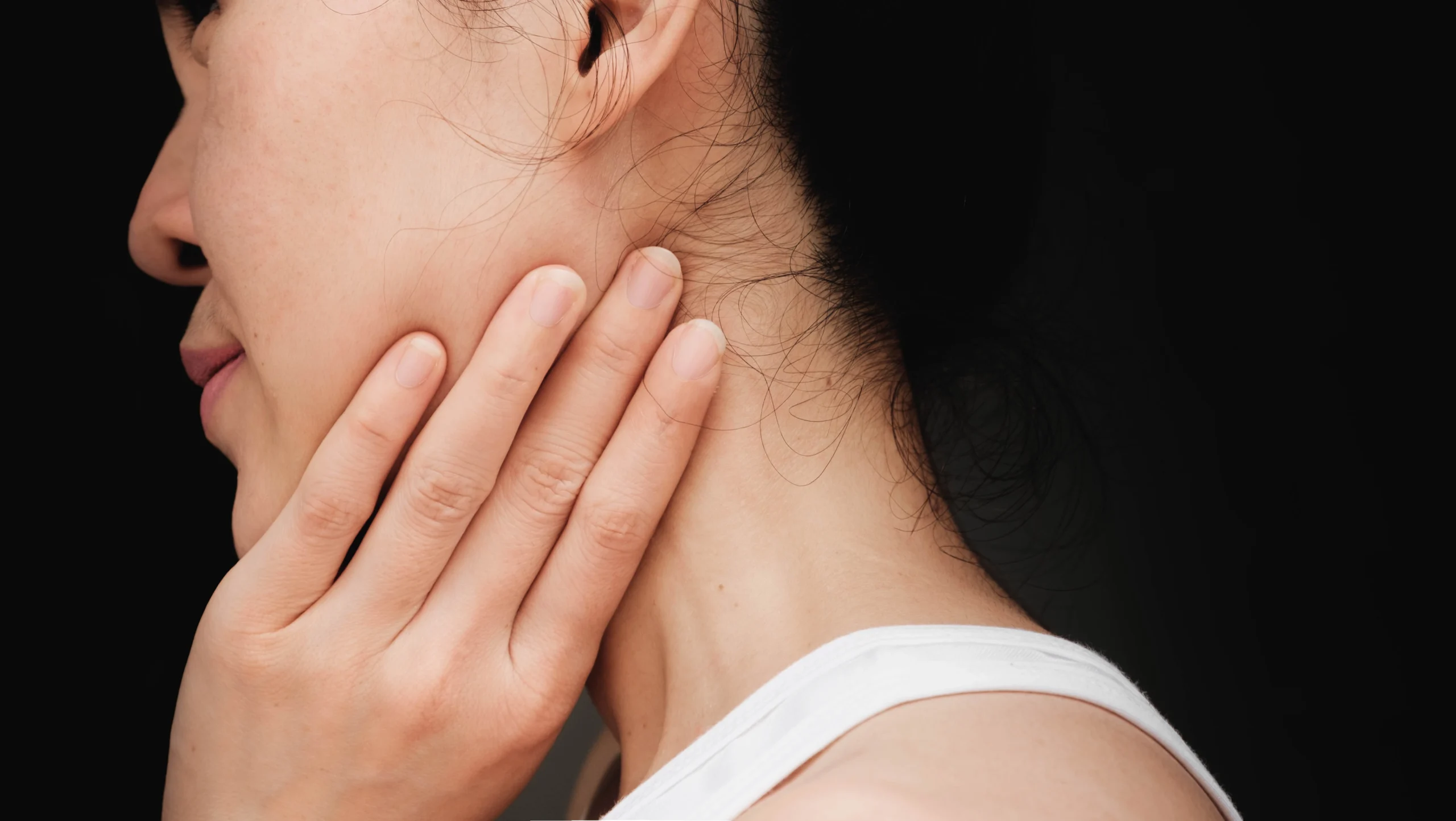
Salivary glands produce saliva, a vital fluid that helps with digestion, keeps the mouth moist, and protects teeth from decay. These glands are made up of specialized tissues that secrete enzymes and other substances essential for breaking down food. By maintaining oral health and aiding in swallowing, salivary glands play a key role in the body’s digestive and protective processes.
Minor and Major Salivary Glands
Common Salivary Gland Disorders
Dry Mouth
Salivary Gland Stones
Lumps (Noncancerous Tumors)
Lumps can also be present in salivary glands. These are typically benign masses that cannot spread to other areas, but they do grow over time. Most of the time, we recommend either an ultrasound or a CT scan to examine the mass more closely, as well as a small biopsy of the area. It is crucial to see one of our providers or another ENT specialist as soon as possible if you notice a lump in one of your salivary glands.
Salivary Gland Cancer
Salivary Gland Infections
Salivary Gland Swelling
Risk Factors for Salivary Gland Diseases
Older Age
Dehydration and Malnutrition
Diabetes
Sjögren's Syndrome
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV/AIDS)
Bulimia Nervosa and Other Eating Disorders
Kidney Failure
Medications
Bacterial and Viral Infections
Smoking
Radiation Exposure
Receive Excellent Treatment for Salivary Gland Problems at Texas Sinus & Snoring
Conclusion